Response to Climate Change and TCFD Endorsement
Initiatives to Address Climate Change
Under the Tokyo Century Group’s management philosophy, the Group “will work alongside customers in pursuit of their growth as a highly specialized and unique financial services company and will contribute to the creation of an environmentally sound, sustainable economy and society.” We have recognized that addressing climate change is important for creating an environmentally sound, sustainable economy and society, identified materiality (key issues) linked to the SDGs, and have been working on these issues.
Tokyo Century announced its endorsement of the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures* (TCFD) in April 2021. In addition, based on the results of a risk materiality assessment related to climate change, we identified climate change risks and opportunities under multiple scenarios such as the Sustainable Development Scenario (“well below 2°C” Scenario including 1.5°C) and the New Policy Scenario (4°C Scenario) published by International Energy Agency (IEA) and conducted qualitative and quantitative business impact assessments for the environment and energy businesses (solar power generation) (May 2021), the aviation business (aircraft leasing) (April 2022), and the Automobility business (corporate and individual auto leasing) (April 2023) in line with TCFD recommendations.
We will continue contributing to the realization of a decarbonized society by promoting sustainability management through our business activities, including renewable energy businesses such as solar power generation. Going forward, we will further consider how to address risks and seize opportunities as well as expand businesses subject to scenario analysis while also improving the accuracy of the analysis.
- *Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
Established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) at the request of the G20 to review how climate-related information should be disclosed and how the financial sector accounts for it. In June 2017, it published recommendations on corporate disclosure of climate change initiatives.
Governance
In the governance system of the Tokyo Century Group, the Sustainability Committee, responsible for planning, promoting, and overseeing Group-wide sustainability activities, deliberates the sustainability management strategy on climate change risks and opportunities. Key issues are reported to and discussed at the Management Meeting and the Board of Directors Meeting.
The Sustainability Committee is chaired by the president of the Corporate Planning Unit and composed of relevant officers and the presidents of each unit. The Sustainability Management Division in the Corporate Planning Unit serves as the secretariat, and the committee meets in principle twice a year. It works under the supervision of the Board of Directors to strengthen the PDCA cycle for sustainability management.
Scrollable horizontally
| Main Agendas Related to Climate Change Responses (Fiscal 2022) | |
|---|---|
| Board of Directors and Management Meeting |
|
| Comprehensive Risk Management Committee |
|
| Sustainability Committee |
|
Related Pages
Strategy
The Tokyo Century Group uses a materiality map to verify the importance of issues from the perspectives of Tokyo Century and its stakeholders and determines the five areas of materiality (key issues), which include climate change measures, that correspond with the SDGs. The Group then pursues sustainability management to promote businesses that contribute to the sustainable development of society in collaboration with partner companies.
Materiality (Key Issues) and the SDGs
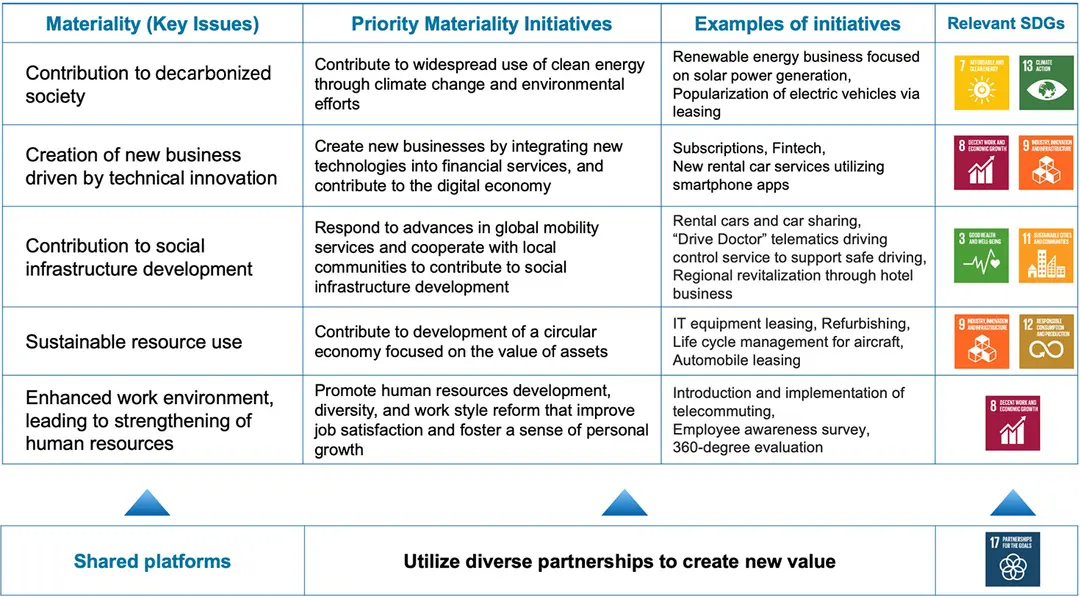
Related Pages
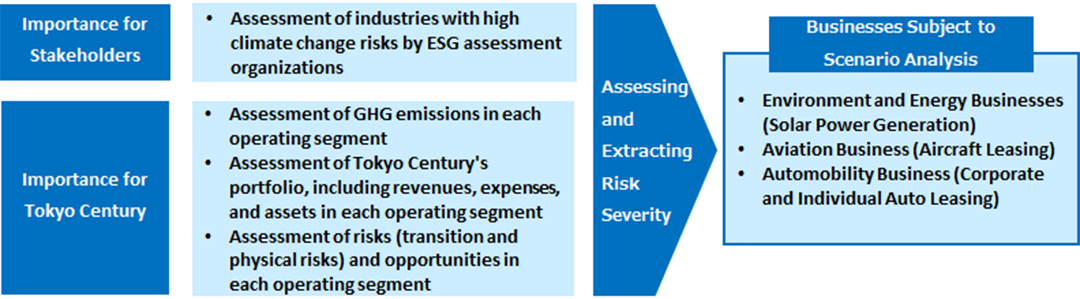
The Tokyo Century Group recognizes climate change as one of the most important social issues facing global society. It is therefore a key management issue in the Group’s materiality as a “contribution to a decarbonized society.” Recognizing this, the Tokyo Century Group conducted a risk materiality assessment from the perspective of its stakeholders and the Group for businesses with particularly high climate change risk within its operating segments.
As a result of the assessment, we conducted scenario analyses for the environment and energy businesses (solar power generation) (May 2021), the aviation business (aircraft leasing) (April 2022), and the Automobility business (corporate and individual auto leasing) (April 2023).
Risk Materiality Assessment
We conduct the scenario analysis in accordance with TCFD recommendations following the four processes below.
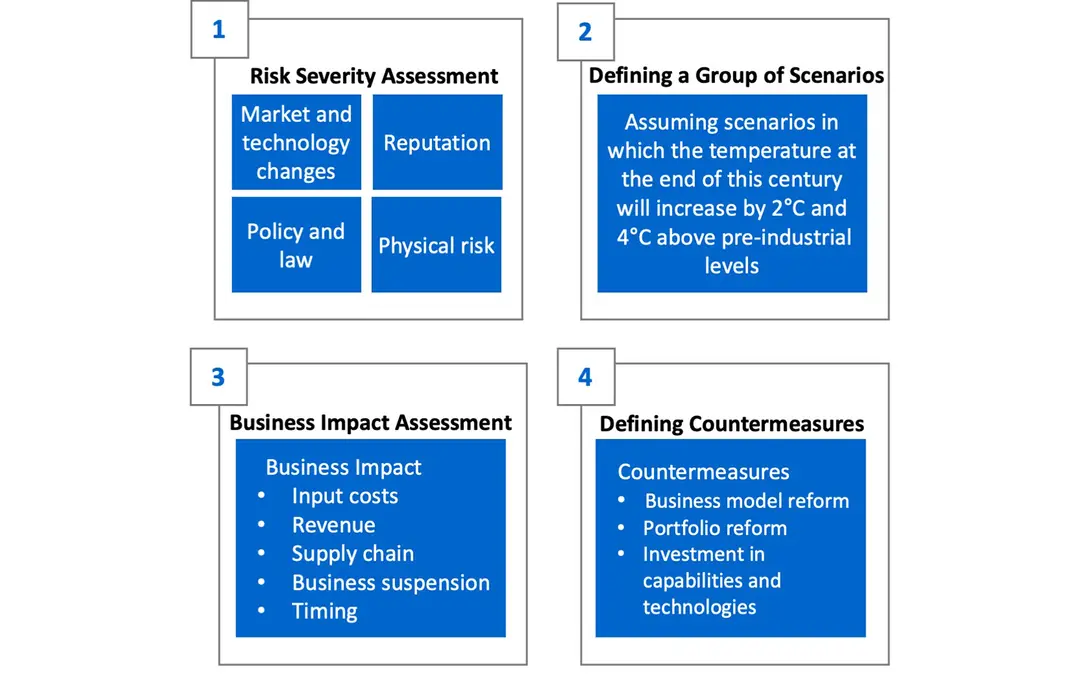
Major Climate Change Risks for Businesses Subject to Scenario Analysis
- Regarding the environment and energy businesses (solar power generation), we recognize the physical risks of urgency due to abnormal weather such as typhoons and heavy rain and the transition risks such as introducing a carbon tax and strengthening laws and regulations.
Scrollable horizontally
Items Details Timeline Risks Opportunities Responses Policy/Legal
(transition risks and opportunities)Subsidy policy for renewable energy, etc. 2040 - The profitability of a business operated under the FIT program may deteriorate if grid parity is not achieved before the program ends
- A stricter CO2 emission reduction policy will be adopted, and the FIT program will provide opportunities for business expansion for a long time to come
- Maximizing power generation efficiency through accumulated asset management expertise
- Developing new businesses in areas such as corporate power purchase agreements, self-wheeling models, and virtual power plants (VPPs)
- Examining renewable energy businesses other than solar power generation
Industry/Market
(transition risks and opportunities)Changes in energy mix 2040 - Due to changes in the energy mix, the number of renewable energy power generation companies will increase, and the competitive environment will become increasingly severe
- Sales prices may fall
- Japan has stipulated that the share of non-fossil electricity in electricity sales should be 44% by 2030, and opportunities for renewable energy generation will expand
Acute
(physical risks and opportunities)More severe abnormal weather 2040 - Damage to employees and power plants caused by torrential rains, floods, and typhoons will result in shutdowns, lower operating rates, and additional investment to restore facilities
- Insurance premiums and other costs will increase for assets located in high-risk areas
- The development of resilient equipment through the accumulation of expertise may lead to new opportunities via the external supply of this equipment
- With regard to the aviation business (aircraft leasing), we recognize the physical risks that will be incurred due to the impact of severe extreme weather events and the transition risks such as carbon emission targets in each country and regulations unique to the airline industry.
Scrollable horizontally
Items Details Timeline Risks Opportunities Responses Policy/Legal
(transition risks and opportunities)Aviation industry regulation (CORSIA) 2050 - Potential restrictions on financing/lending and leasing to airline companies that do not meet the standards
- Securing a sufficient number of next-generation aircraft*1 will increase earnings opportunities
- Reduce portfolio risk by diversifying and expanding lessee base and shifting toward next-generation aircraft
- Enhance the asset turnover business to realize the early sale of owned aircraft and improve profitability
- Expand asset management business extended to third parties post sale of aircraft
Technology
(transition risks and opportunities)Spread of next-generation aircraft*1and new generation aircraft*2 2050 - Potential rapid decline in value of current next-generation aircraft*1
- Potential increase in earnings and asset value from an owned portfolio with a sizable number of new generation aircraft*2
- *1Next-generation aircraft: Low-carbon aircraft based on improved fuel efficiency, lighter body, and other features
- *2New generation aircraft: Blended wing body passenger aircraft, alternative fuel aircraft, electric aircraft, hydrogen-powered aircraft, etc.
- Concerning the Automobility business (corporate and individual auto leasing), we recognize the physical risks resulting from the impact of severe extreme weather events, such as vehicle production delays due to flooding and heavy rainfall, and the transition risks of shifting from gasoline and diesel vehicles to EVs, such as switching from fueling to charging.
Scrollable horizontally
Items Details Timeline Risks Opportunities Responses Policy/Legal
(transition risks and opportunities)National carbon emissions targets and energy saving policy 2040 - Further shift to EVs may result in lower-priced used gasoline and diesel vehicles
- Demand for used EVs may increase and prices for used EVs may rise after lease expires
- Strengthen the value chain to launch new EV-related services for corporate and individual customers
- Establish an appropriate maintenance system for EVs
- Expand the use of preferential interest rates for procuring EVs through the issuance of green bonds
- Strengthen the monitoring of changes in the used vehicle market for gasoline, diesel, and EVs and set appropriate residual values
Industry/Market
(transition risks and opportunities)Changes in customer behavior 2040 - Increased environmental awareness among customers may reduce demand for gasoline and diesel vehicles
- Increased environmental awareness among customers could strengthen demand for EV leasing
Industry/Market
(transition risks and opportunities)Products and services 2040 - Widespread use of EVs, which have fewer parts than gasoline and diesel vehicles, may reduce maintenance revenues
- Shift to EVs could generate new earnings opportunities, such as recharging services and businesses for second-life EV batteries
Acute
(physical risks and opportunities)Intensified extreme weather 2040 - Heavy rainfall and flooding may cause vehicle production delays and damage leased vehicles

Scenario Analysis Details
Please refer to the link below for details by business subject to scenario analysis.
- Environment and energy business (solar power generation) (1,074KB)
- Aviation business (aircraft leasing) (588KB)
- Automobility business (corporate and individual auto leasing) (1,592KB)
Risk Management
The Tokyo Century Group has established the Basic Risk Management Policy and set up its Comprehensive Risk Management Committee to identify and evaluate Group-wide risks that may significantly impact management and to appropriately address both qualitatively and quantitatively as necessary to implement comprehensive risk management.
The Group has developed a risk heat map by assessing the yearly changes in its business for risk categories set forth in the Basic Risk Management Policy and the Comprehensive Risk Management Rules. It is also developing a matrix that will measure the level of impact and frequency of occurrence. Climate change risk is mapped on the heat map based on our assessment as a non-financial operational risk.
We have also established a system for monitoring operational risks, including climate change, and results are reported to the Board of Directors twice a year through the Comprehensive Risk Management Committee as a risk index for non-financial information.
Preliminary measurements of exposure to transition risks and physical risks are conducted and the results are reported regularly to the Comprehensive Risk Management Committee to determine the potential impact of climate change risks on Tokyo Century’s credit portfolio.
Exposure to transition risks is quantified through Monte Carlo simulations targeting sectors chosen based on TCFD recommendations after accounting for the potential impact of these risks on debtor ratings and asset value. Physical risk exposure is measured as the maximum loss projected to be incurred based on statistical simulations of specific business assets (solar power generation businesses, etc.) that have suffered damages from natural disasters.
Related Pages
Metrics and Targets
The Tokyo Century Group announced its carbon neutrality policy for fiscal 2040 in September 2022. The policy describes our goal of achieving effectively zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions while also presenting a transition roadmap for the biomass co-firing power plant owned by Shunan Power Corporation, a consolidated subsidiary of Tokyo Century, which accounts for approximately 98% of the Group’s GHG emissions. The Transition Roadmap has received “Green 1 (T) (F)” for the highest overall evaluation of the Climate Transition Finance Evaluation by Japan Credit Rating Agency, Ltd.
In addition, the Tokyo Century Group is working to reduce its environmental load by adopting an ISO 14001-certified environmental management system (EMS) based on its Basic Environmental Policy.
We have set targets for contributing to environmental well-being through our business activities, including office activities and renewable energy business, and continuously manage these activities by calculating annual CO2 emissions. In fiscal 2023, electricity consumption* was 28,434,000 kWh, CO2 emissions (market-based) were approximately 13,075 t-CO2, annual energy production through our solar power generation businesses (nine consolidated subsidiaries including Kyocera TCL Solar LLC) was 560,000 MWh, and contribution to reductions in CO2 emissions was 218,000 t-CO2.
- *The target companies were those within the scope of the EMS plus our consolidated subsidiaries in Japan, which manage the related data.
Related Pages
Related Materials


