What Are the Implications of a Decarbonized Society: Global Trends and Efforts Underway in Japan
Jun 9, 2021
Nations around the world are pursuing strategies for achieving the vision of a decarbonized society, in which greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change are reduced to net zero. Why is it so important to realize such a society? Is it possible? In this article, we answer these questions and review the global trends toward a decarbonized society as well as efforts underway in Japan.
Global Warming Has Become a Major Concern Worldwide as Rising Temperatures Cause Disasters and Droughts and Destroy Ecosystems

Why is the world now working to realize a decarbonized society? The reason is very clear. Climate change associated with greenhouse gases has become a serious concern.
The average global temperature is reported to have risen by 1.1°C over the past century due to the ongoing emission of greenhouse gases related to human activity since modernization after the industrial revolution. This rise in temperature has led to an increase in extreme weather events around the world. The frequent occurrences of torrential rainfall and powerful typhoons in recent years are believed to be consequences of climate change.
If this situation is allowed to continue, rising sea levels will inundate the shorelines of many countries, and many life-threatening disasters such as storm surges, floods, typhoons, and heat waves will happen more often. Food shortages due to drought will worsen, leading to intensified social conflicts. The global environment will undergo irreversible damage as ecosystems are destroyed.
Global warming has already emerged as a matter of human survival, and the international community must place top priority on addressing this problem through a concerted effort. This is universally acknowledged, in both developed and developing countries.
The Paris Agreement was adopted at the United Nations Conference in 2015 to address global warming. For the first time in history, every country, including developing nations, participated in the international framework on post-2020 climate change. The Paris Agreement set the goal of holding the increase in the average global temperature to well below 2°C above preindustrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
Initiatives and Technologies for Attaining Carbon Neutrality by Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions to Zero
Countries around the world are currently working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions under the Paris Agreement. Japan has set a goal of reducing its emissions by 46% from the 2013 level by 2030.
In addition, most developed countries have declared their goal to become carbon neutral, which means achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions overall, and in a policy speech to the Diet in October 2020, Prime Minister Suga also expressed Japan’s commitment to become carbon neutral in terms of net-zero emissions by 2050.
Some might think that achieving zero greenhouses gas emissions is impossible. This goal would indeed be impossible as long as we continued to live a civilized life. However, what Japan and other countries are declaring is that they want to achieve net-zero emissions.
While concern has focused on the emission of greenhouse gases, they can also be absorbed and removed. For example, we can plant trees that absorb CO2 through photosynthesis. There is also a negative emission technology for capturing CO2 in the atmosphere and storing it safely. These efforts and technologies, along with reduction measures, could ultimately bring down the total volume of greenhouse gas emissions to zero. This is what is meant by carbon neutrality.
Global Trend toward Carbon Neutrality Opens the Opportunity for a New Growth Strategy

Carbon neutral is now a major global trend, and more than 120 countries and regions have already declared their intention to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
Europe, where environmental awareness has always been high, is strongly encouraging renewable energy, electrification policies, and the use of recycled materials under its long-term strategy for 2050. In the U.S., although former President Trump decided to withdraw from the Paris Agreement, the Biden administration is determined to return. Biden is positioning climate issues as a vital aspect of his foreign policy and national security while pursuing a variety of measures.
China, viewed as among the leading emitters of greenhouse gases, has also announced its intention to become carbon neutral by 2060, along with its goal of reducing CO2 emissions in relation to GDP by 60% to 65% from 2005 levels by 2030.
The quest for carbon neutrality has sparked international competition as nations view the creation of a decarbonized society as an opportunity to be capitalized on for new growth strategies. Achieving carbon neutrality will require technological innovation, and current social and economic structures will need to undergo dramatic change.
All of this represents a significant opportunity to encourage new investments, transform the industrial structure, and improve productivity. This is why corporations and financial institutions around the globe are following the trend toward a decarbonized society and expanding environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investments.
Major Challenges for Japan in Reducing Thermal Power Generation and Expanding Solar Power and other Renewable Energy Sources

The actions required for creating a decarbonized society are clear. First, we must reduce the energy consumption of society as a whole. To that end, we need to promote more energy-efficient lifestyles, social structures, and products.
The widespread use of electric vehicles (EVs) and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), the electrification of household water heaters and stoves, and the introduction of hydrogen fuel cells would also be effective. More importantly, we need to decarbonize the electric power sector, which emits massive volumes of greenhouse gases, and increase the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass.
How far has Japan advanced in its efforts to realize a decarbonized society? The Japanese people have traditionally valued living in harmony with the environment. Japan possesses sophisticated energy-saving technologies and is actively pursuing research and development into establishing a hydrogen-based society, including fuel cells. The major bottleneck, however, has been the lack of natural resources.
Going forward, Japan’s greatest challenges will be to gradually reduce dependence on coal-fired power and expand the use of renewable energy sources such as solar power.
Tokyo Century Contributes to the Creation of a Decarbonized Society through Solar Power Generation
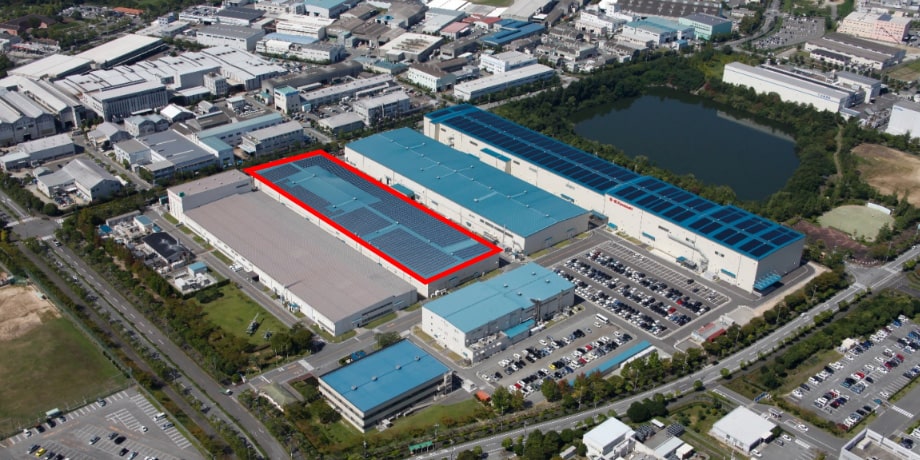

Seishin Works, Kawasaki Heavy Industries (The red frame indicates the area in which the new system will be installed)
The role of companies in creating a decarbonized society is just as important as that of the government and administrative agencies. Many Japanese companies have set their own targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and are striving to contribute to the creation of a decarbonized society through their business operations.
One such example is the solar power panel business that Tokyo Century is developing with Kyocera Corporation. The widespread use of Kyocera’s high-quality, highly durable panels will be extremely beneficial in the long-term reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
The initial cost of introducing solar power generation has been a bottleneck for businesses. To address this, Tokyo Century is offering a service in collaboration with the Kyocera Group that allows customers to introduce solar systems without any initial investment by assuming responsibility for the installation, maintenance, and management costs. In 2020, this service facilitated the installation of solar power generation equipment on the rooftop of the Seishin Works of Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Furthermore, we launched a new renewable energy business in collaboration with a Tokyo Century Group Company, Shinko Real Estate Co., Ltd. Solar panels will be installed on real estate owned by Shinko Real Estate as well as on land and buildings to be developed in the future. The electricity generated by the panels will be more than sufficient for the hosting sites, with the surplus distributed to other facilities.
Tokyo Century is committed to playing its part in realizing a decarbonized society through its business operations under its management philosophy of creating an environmentally sound, sustainable economy and society.
For more details on the Tokyo Century Group’s sustainability initiatives, see:
https://www.tokyocentury.co.jp/en/csr/
*The contents of the article and the position titles are as of the date posted.
RECOMMEND ARTICLES

—Exploring the Communication Required to Become a Truly Global Company
Aug 21, 2024
Communication has be…

Dec 20, 2023
New risk factors hav…






