
What Kind of Company Encourages Employees to Work Vigorously? Happiness Planet CEO Kazuo Yano Shares His Views on Creating an Organization Grounded in Well- Being.
Jan 17, 2024
With new ideas emerging about the essential nature of companies and the way people work, Tokyo Century is also striving to create a workplace environment that is conducive to well-being. What is it about an organization that enables people to be happy and productive? To gain some insight in this area, Tokyo Century NEWS invited Mr. Kazuo Yano, Fellow of Hitachi, Ltd. and Representative Director and CEO of Happiness Planet, Ltd., who has been focusing on realizing organizations that promote well-being by applying technology and data, to present a webinar. In this article, we take a look at his presentation.

Importance of Balancing Risk and Development Modes
The pace of change has been so rapid that it would have been difficult to even imagine today’s world 50 years ago. These changes have been driven by technology, and technological advances have been reshaping our world at an accelerating rate.
As we live through this era of drastic change, we need to steadfastly carry out our daily work while at the same time flexibly adjusting our direction in the face of change by asking if we are still working the right way.
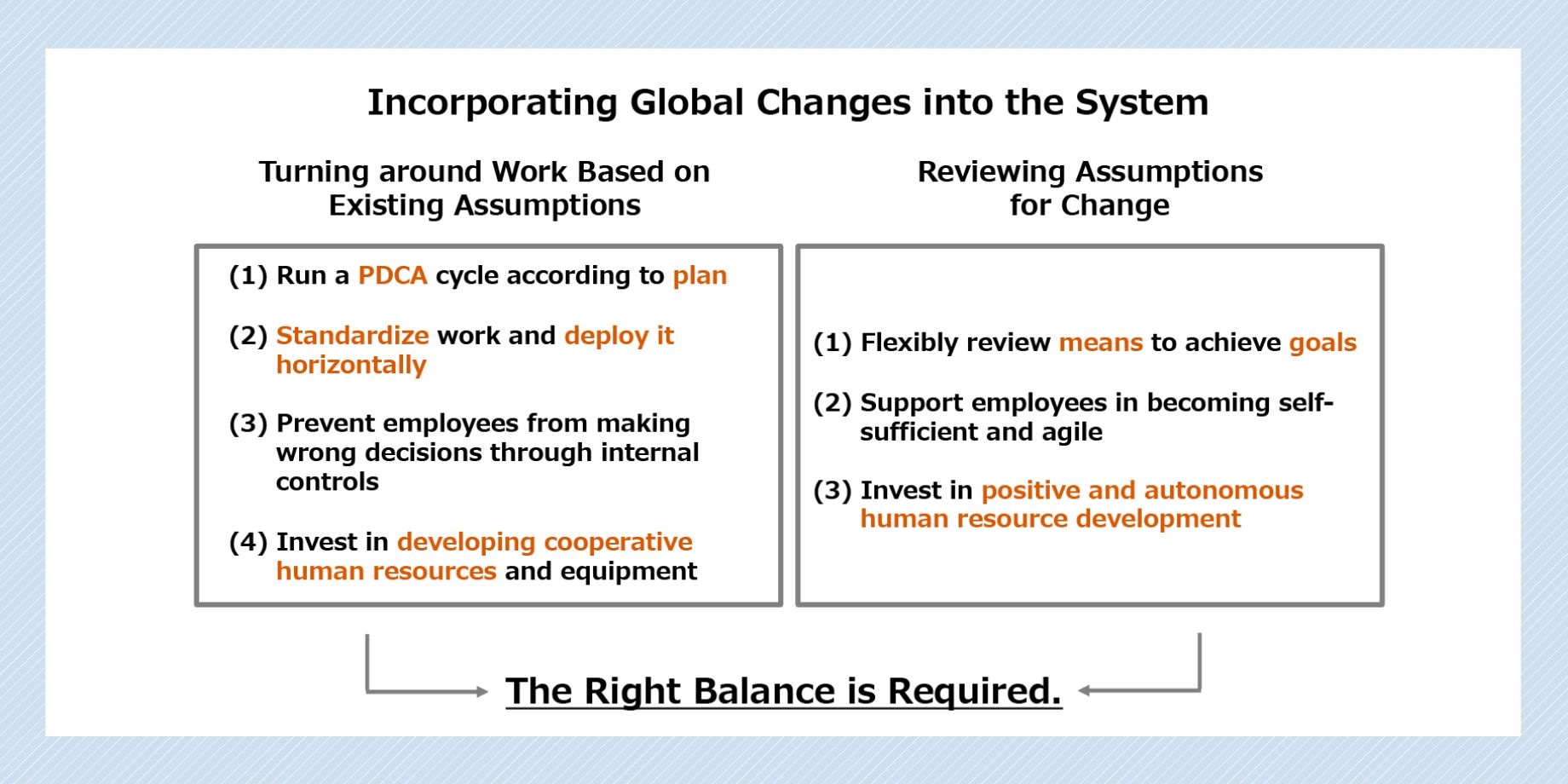
Our conventional way of working is displayed on the left side of the above diagram. These kinds of jobs are based on existing assumptions; however, they are not enough alone. As shown on the right, it has become important to review existing assumptions in the face of change.
When we try to work under existing assumptions, shown on the left, we inevitably focus on avoiding risks and threats. This is because our brains are wired to avoid risk in order to survive. These risk mode circuits also focus on immediate threats, narrowing our vision and raising our blood pressure and heart rate to generate feelings of anxiety or worry.
On the other hand, as shown on the right, the development mode circuit is operating. In this mode, you can discern clues to solving problems, experience enthusiasm and enjoyment, and find room for ingenuity. This development mode circuit is believed to be the source for growth and collaboration.
This does not mean that risk or development is more important; the key is in maintaining the two modes in harmony and balance. The point at which they are in balance is referred to as a state of well-being.

I have seen large Japanese companies controlled by risk mode in order to avoid failures and losses. But this is out of balance with the development mode and does not lead to a state of well-being. Of course, shifting to the development mode entirely is not good either, as this increases the risk of poor control and management, leading to scandals and other harmful incidents. Again, the key is finding the balance between risk and development.
We Are Not Happy Because We Have Done Well; We Do Well Because We Are Happy
In these times of change, we are forced to reconsider the meaning of our work. By working and making profits, the world becomes richer, and as a result people become happier. The understanding that this cycle makes us happy was dominant in the 20th century.
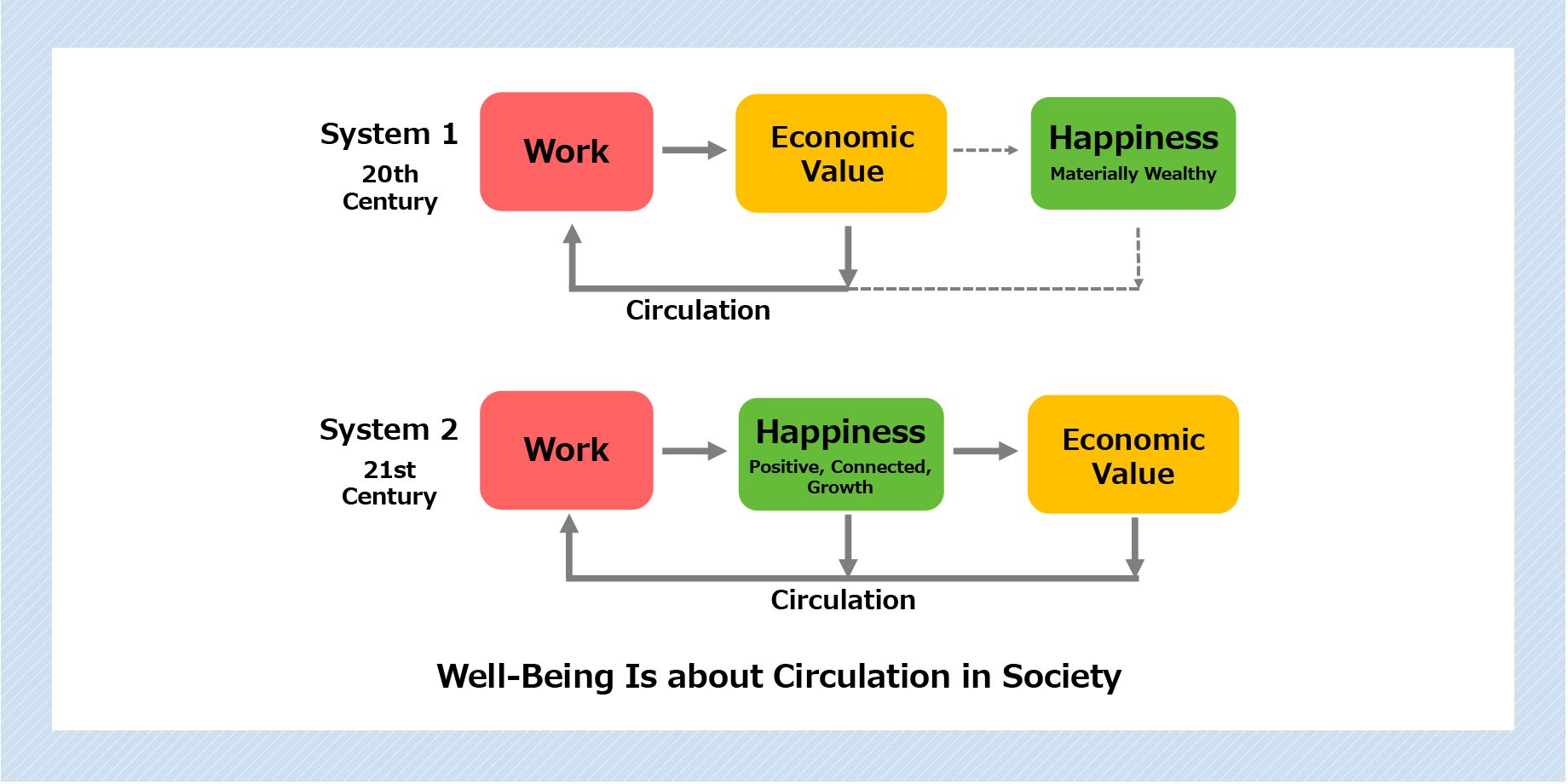
What has become important in the 21st century is the understanding that people can establish their own role and place in the world through their work, and that being able to use their ingenuity and take on various kinds of challenges will lead to one’s own happiness and sense of fulfillment. These positive challenges will generate economic value and ultimately create new profits and jobs―a positive cycle.
Does economic value create happiness or does happiness create economic value? I think that is the main difference. Generally, happiness is considered to be a vague, subjective, and individual concept. This, though, is incorrect. The variety of data we have been able to collect has strengthened our ability to recognize the source of happiness.
For example, many people think they are happy when they are successful at work, or when they are healthy. But experiments have shown that the opposite is true, that in fact happiness makes you successful at work and makes you healthy. Even in the world of business, data shows that the average order rate can vary by 31% depending on the salesperson’s relative level of happiness, and that when salespeople are happy, creativity is three times higher and the turnover rate is lower.

Four “HERO” Skills to Be Positive
Some people may feel a gap between the harsh business world and the concept of happiness. The key here is that happiness is not about being comfortable; it is about being positive. Conversely, it can be said that a backward-looking state of anxiety, distrust, and skepticism is an unhappy state.
Many people tend to have the mistaken idea that being positive is a personal characteristic, but it’s really a skill that anyone can acquire through training, just as anyone can learn to drive a car with practice.
So, then, what skills do we need in order to be positive? There are four major skills, summarized by the acronym HERO (capital of the mind).

1. Hope
The power to believe that a path can be found. The ability to believe that there is a way because the future is unpredictable.
2. Efficacy
The power to accept reality and take the first step. The ability to take action where you are, rather than waiting until everything is in place.
3. Resilience
The power to face difficulties. The ability to face challenges without running away even when things do not go well. The ability to create a positive story in the midst of difficulties.
4. Optimism
The power to enjoy any situation. The ability to take advantage of chance opportunities and encounters, and to recognize opportunities in the midst of change.
Positivity, as demonstrated through HERO behavior, can be consciously changed in a short period, while personality and character are difficult to alter and could be said to be completely different than positivity. Data shows that personality and character are hard to change through personal decision, so it’s better to make the most of one’s unique personality and character.
You should also have a positive attitude to make the most of your own individuality and, by extension, the individuality of others. This is exactly what it means to make the most of human capital. In this age of diversity, it is no longer easy to succeed in business while ignoring each other’s individuality.

Triangular, Not V-Shaped, Relationship Is Important in an Organization
So what is needed to enhance such positivity? The answer is good relationships. These are essential for people to experience happiness.
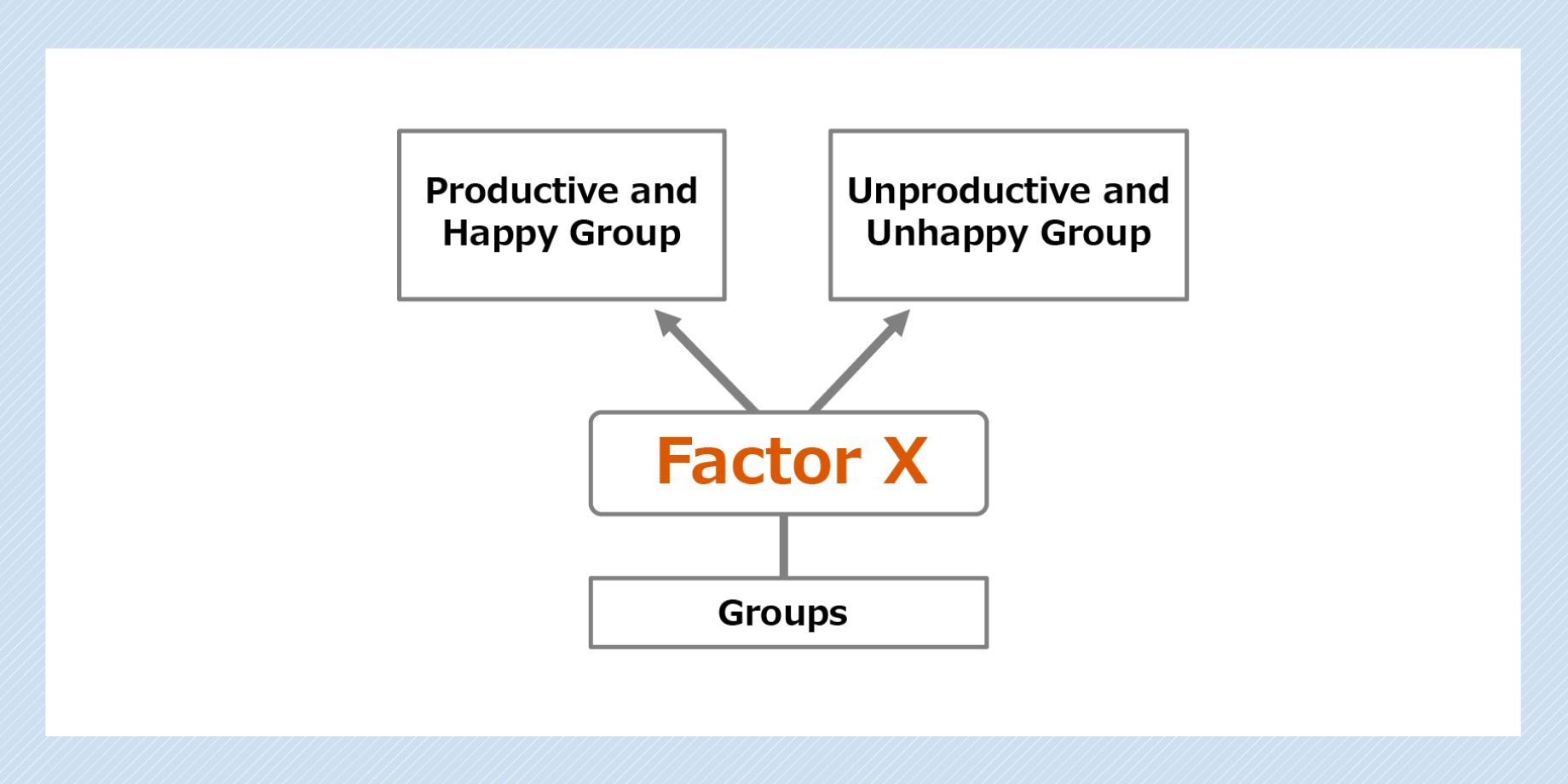
To grasp the essence of good human relationships, I collected more than 10 trillion data points from various occupations and organizations on “who communicates with whom and when” and “how people move” over a total of more than 10 million days.
By analyzing the data, we were able to identify an extremely important factor that separates the productive and happy group from the one that is unproductive and unhappy. We named this differentiating factor Factor X.
While communication is essential for good relationships, the amount, whether it’s a lot or a little, is completely irrelevant. Now imagine three people. Suppose one is talking separately with Partner 1 and Partner 2. This is a V-shaped relationship.
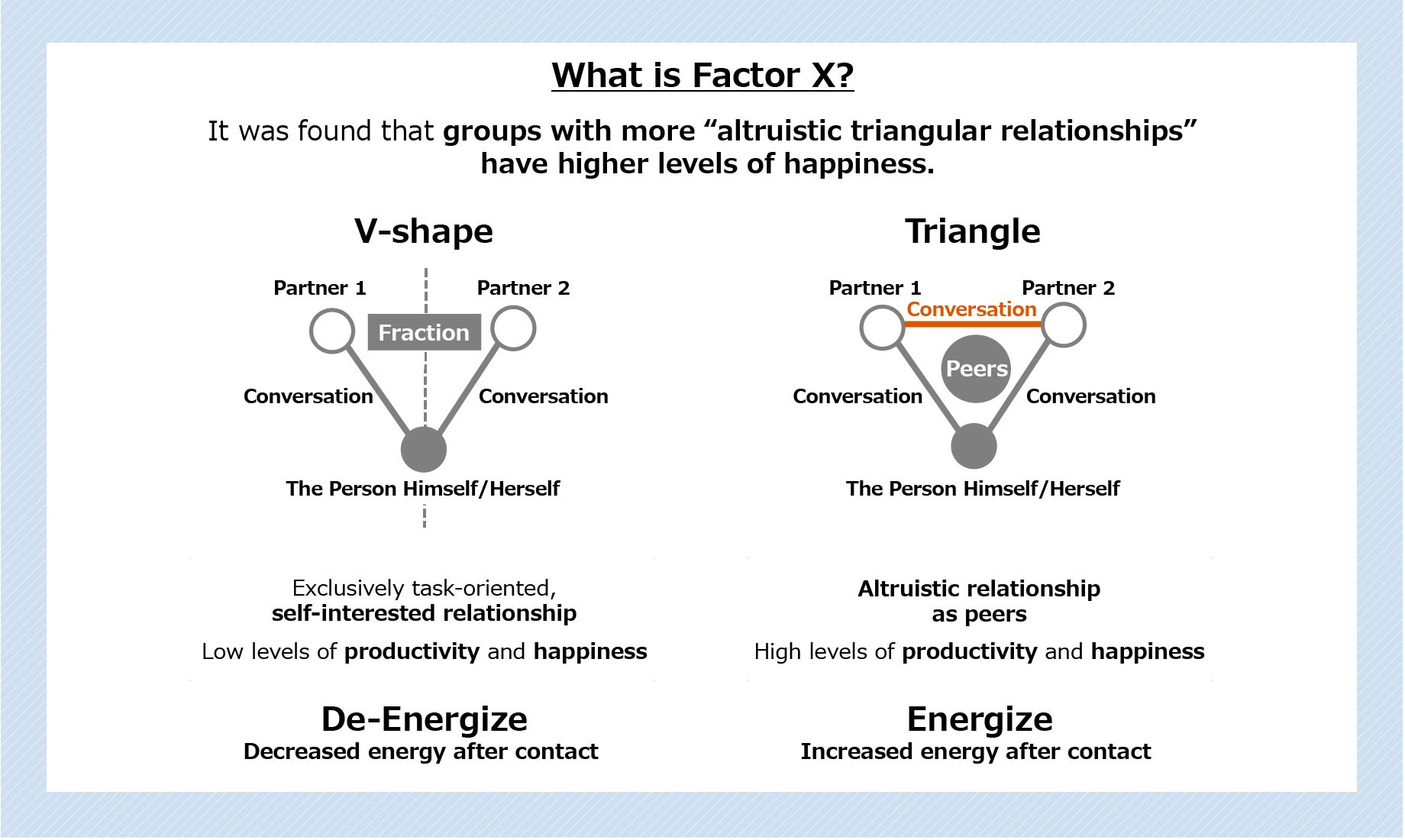
Suppose that Mr. A participates in a project with Mr. B, the project leader, and with Mr. C, a supervisor who separately evaluates Mr. A. Although Mr. A has to talk with both Mr. B as project leader and Mr. C as supervisor, Mr. B and Mr. C don’t have a relationship beyond their work, nor do they talk to each other at all. This is a V-shaped relationship, and Mr. A tends to be depressed.
When Mr. B and Mr. C do talk to each other, a triangular relationship is created. This can be established altruistically and leads to high productivity and happiness. Furthermore, they can experience empathy and solidarity as individuals and as peers.
In the course of doing our work―although we must report, provide instructions, make requests, and respond to business matters―these interactions alone are not enough. We must also establish solid interpersonal relationships that view our connections as peers. Interestingly, some data shows that those in V-shaped relationships lose physical energy after contact, while those in triangular relationships gain energy.
The small difference between a human relationship that is V-shaped or triangular can make a big difference in whether someone feels depressed or is able to work with vigor. This is also based on data.
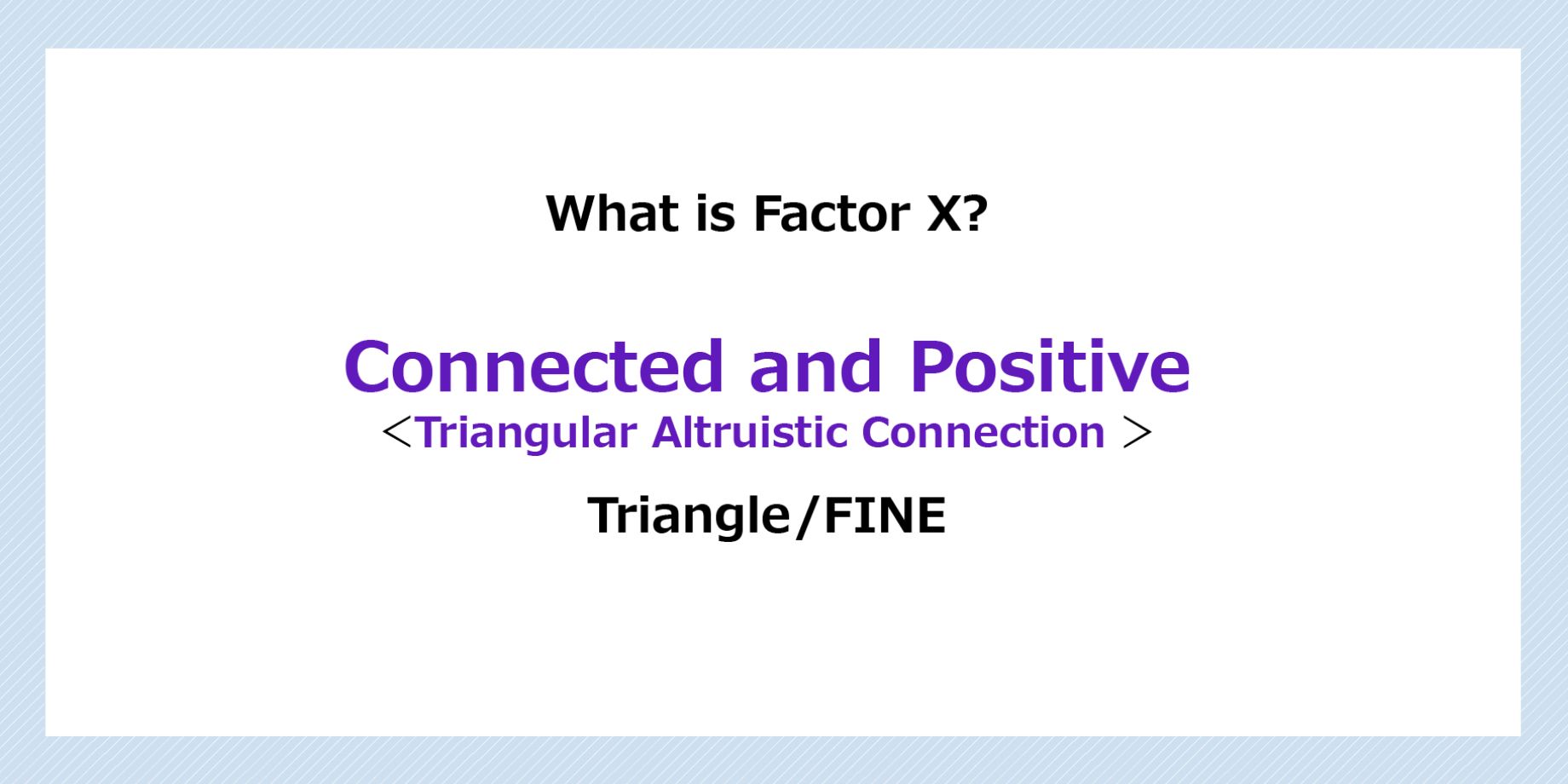
In this context, what is the Factor X mentioned earlier? The answer is “connected and positive,” meaning that connections are being built that are not just about tasks or profit and loss. To realize these relationships in the workplace, we must have both “involvement = tasks, efficiency, risk avoidance, V-shape” and “connection = self-disclosure, trust/empathy, cooperation/development, triangle.” These are important to establish triangular human relationships.
What Sports Have But Work Does Not Is a Cheering Section of Supporters
Any deterioration in the quality of communication will cause company performance to suffer. It’s difficult, however, to simply expect improvement in the quality of productivity and communication. First, people must be proactive and enhance the quality of their mutual relationships. After that, the quality of communication, productivity, and economy will also rise.
To this end, I developed an app that creates opportunities for employees to talk with each other. For example, the AI asks, “Tell me about a book you recently read,” to which you comment on what you have read and what you thought at the time. In response, those around you can add comments of support and empathy. These kinds of opportunities and subjects create connections, although it’s all too often the case that employees may work together for years and still not know anything about the personalities of their colleagues.

There’s one thing that sports have and that businesses do not, and that is a support by cheering. So, we first form groups of about ten members to cheer each other on, as it would be difficult for a thousand employees to do that. By assigning priority to the groups that have established internal triangular human relationships to become a team, and changing team composition from week to week, we generate many triangular relationships within them. By rearranging the groups themselves, we can also create a group of one thousand employees with many acquaintances of acquaintances.
Generating a lot of natural triangular relationships in this way to create a state of well-being is important for any organization. Establish horizontal connections and not just vertical ones. This is possible with the use of technologies and other tools.
Society and companies are made up of people, and people can be completely different depending on their mindset. This is not just a psychological theory, and it’s more than merely relationships; connections are the key and the quality of those links can make all the difference.
Every person can achieve well-being, and there’s definitely something you can do starting today. It doesn’t matter how small, just keep building on it. I believe that’s the first step toward achieving well-being.

Kazuo Yano
Fellow of Hitachi, Ltd. and Representative Director and CEO of Happiness Planet, Ltd.
Mr. Yano developed a technology to quantify happiness based on unconscious physical movements and also established Happiness Planet, Ltd. in 2020 to commercialize the technology. He has played a leading role in the development of multi-purpose AI and sensors that quantify happiness.
Note: The contents of the article and position titles are current as of the date posted.
RECOMMEND ARTICLES

Dec 13, 2024
Since fiscal 2022, T…
Feb 28, 2024
With the Act on Chil…




